Classification of Dobby:
INTRODUCTION: -
Dobby is a shedding device
attached to the loom to increase the design capacity. The dobby normally
controls 12 to 24 hold shafts the dobbies are classified as negative or
positive, single lift, double lift, crank driven, cam driven, etc.
The dobby forms a bottom closed,
center closed, semi-open, and open type of shed. The dobby is also classified as
left hand and right hand.
The right-hand dobby is placed at the left-hand side of the left hand. It gets driven from the left-hand
end loom.
The left-hand dobby is one placed
at the right-hand side of the left-hand loom. The left-hand dobby gets its drive from the right
end of the loom.
Difference between tappet and dobby shedding:
|
Tappet Shedding |
Dobby Shedding |
|
Tappet shedding is simple and cheap in construction. |
Dobby shedding is relatively complicated. |
|
Tappets produce simple and basic designs using a
maximum of only eight heald shafts. |
A dobby can produce small motifs using many more
heald shafts up to a maximum of 40. |
|
A tappet loom works efficiently and consumes less
power. |
A dobby loom consumes more power. |
|
A tappet loom can be run at high speed with less
machine vibration. |
A dobby loom cannot be worked at high speed because of
high machine vibration and excessive friction between moving parts. |
|
Tappets are required to be changed for altering the
design gearing on the bottom and counter shafts are to be altered. |
The designs can be modified easily change out is
brought about quickly and does not require any major alternation |
|
The number of heald shafts used and picks/repeat
cannot be changed for a given set of tappets. |
The number of healds and picks/repeats can be easily
altered. |
|
In a tappet, the shedding dwell period is maintained for
the safe passage of the shuttle. |
In swing lever dobbies there is no dwell period. In
a cam dobby, a dwell is maintained. |
Climax Dobby
The Climax Dobby is a double-acting machine controlled from the bottom shaft, it forms the open shade. The lifting of heald is done by the lifting of jacks. The healds are lowered because of springs used on the bottom side. It has 2 jacks. Dobby runs at half the speed. In the right-hand dobby, the cylinder rotates in a clockwise direction. In the left-hand Dobby, the cylinder rotates in an anticlockwise direction.
Working
Dobby gets its drive from the bottom shaft through a connecting rod. The T-lever gets oscillation and thereby knives move forward and backward in the framing machine slot. When the knives are towards the set of hooks selection of engagement hook and knife is made feller. The feelers are activated because of wooden pegs. when the hooks and knives are engaged, then the hook is pulled, while the other hook and the lever rest on the stop bar. now the heald is lifted up.
Cycle of lifting of healed into Climax Dobby:
A-The Healds shaft
remains down no selection has taken place.
knives K1 and K2 are about to move from extreme positions.
B-Heald is down
and the hook is not engaged with the knife on the second pick.
C-It represents the engagement of the hook and knives are about
to pull the hook to lift the shed.
D-Heald is lifted up on the pick.
E-The heald is again lifted up on the next pick because of the engagement of hook and knife.
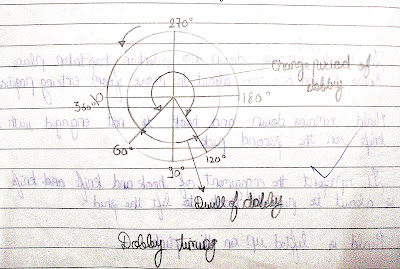
Timing and setting of Climax Dobby:
1-At 270 degrees The heald shaft is leveled, and knives are in the midway position.
2-The T- lever is horizontal. At 60 to 120 degrees is the dwell Period of
the dobby.
- Heald is stationery
- shed shed is open
3-At 90
degrees, one arm of the t— lever is outside and another is
inside.
4-The bottom shaft is at the top or on the bottom center
At 120 To 360 degrees To 60 degrees is the change period of the heald shaft.
Settings:
1- The driving rod connecting to the crank attached to
the bottom shaft of the loop and T-lever must be set to the appropriate
length. If the rod is too short or
long, one set of the hooks will travel more distance than the other.
2- The length of the driving rod is adjusted such that T-Lever is horizontal when the crank attached to the
bottom shaft is in a horizontal plane either in the front or back of rotary its
stroke.
3- Crank and T-lever are kept in the horizontal position and now two knives are Adjusted by draw bolts so that they are equidistant from their slots. The pattern cylinder is
rotated by a ratchet wheel. The cylinder is
rotated by 1/8th revolution for every 2
picks. the cylinder is held steady by a flat steadied star wheel. The Pawl regulates through the star wheel. The
T-lever is lifting knives in are
extreme position there should be a
quarter-inch clearance between the tip
of the pawl and the teeth of the
cylinder ratchet.
For right-hand Dobby visible outermost feeler which operates the bottom drawer hook, the pattern
cylinder rotates clockwise.
In the left-hand Dobby,
the first feeler is a straight
feeler that acts on the top hook.
In pegging, the upper row of holes in the lug represents the first pick.
Cross Border Fabrics:
Many fabrics need a border in the warp as well as in the weft way. for creating the weft way border design. The number of wooden legs required is
high. so to create a border design, a special cross-border Dobby is used. the fabrics that need the cross border are
sarees, carpets, Chadar, tapestries,
handkerchiefs, and table covers.
Cross border Dobby
Cross-border Dobby is used when two different weaves are
required to be woven using the same number of healds.
Cross-border Dobby eliminates the high number of wooden legs
that are required in normal dobbies.
Types of cross-border dobbies:
1- Two cylinder
cross border Dobby
2- Three cylinder cross border Dobby
Dobby Faults:
The common problem in the dobby is Jack missing. The
heald shaft is not lifted when required and the weft floats across the warp end
giving rise to the fabric effect called stitching.
Stitching is sometimes caused by shuttle flying. Warp
thread breaks occur because of shuttle fly causing a major fabric defect.
The causes of Jack's missing (Heald not lifted) are:
1) Bent wooden peg in a lag.
2) The wooden peg is worn out due to frequent use.
3) The spacing between the lag should be uniform and the cylinder should be perpendicularly positioned below the feeler. if
the lags are not spaced properly more feelers may be lifted causing the lifting of
improper jack.
4) The pattern barrel in which the wooden lag rotates should
not move laterally.
5) The needle operating hook may get stuck and the jack is
missed, good oiling is necessary.
6) The wooden peg will be broken and therefore jack is
missed.
7) The hook may come off from the knife in the middle of the stroke, causing a missing jack.
Ruti Cam Dobby:-
The ruti cam dobby is negative in action i.e. the heald are lowered because of the spring in this dobby. The knives are pushed forward by the pair of cams. The knife will come back and always be in contact with the cams because of the spring. Here dwell of about 1/3 pic is achieved. The selection of the hooks is made of paper patterns instead of wooden pegs.
Positive Cam Dobby:-
The positive cam dobby is called positive because lifting and lowering of the heald is made positively. The dobby has a cam that will give oscillation to the griffel and returning bar through the lever i.e. when the griffel is engaged with the hook it will pull one side of the bulk and at the same time return the bar to push the other side of the bulk. Suppose heald is to be kept down on the next pick, the bottom hook will not be engaged in the griffel, it is looked in the locking bar and thus engaged in the griffel, it is looked in the locking bar and thus the other end of the bulk will not move even the upper return bar pushes to the bulk towards the stop and heald will be down. in short, it returns the bar stop and locking bar together making the dobby positive along with grooved cam.











3 Comments
Great post indeed.
ReplyDeleteSuch a detailed Study of Dobby. Thanks for Sharing.
ReplyDeleteVery good content on dobby shedding sir
ReplyDelete