Test
Methods of Geotextiles
Saurabh Deshmukh
Department of Textile
Technology
Veermata Jijabai Technological Institute, Mumbai,India
Geotextiles are thin & strong membrane fabric which is used to
reinforce soil & prevent from damage. It is mostly used for
filtration and separation in the road constructions. Geotextile are ideal materials used for Construction
& infrastructure like roads, buildings, dams and many more.why need of
testing to geotextile material? Because, In order to determine if a geotextile
material is suitable for a particular application it must undergo appropriate
mechanical testing procedures. The most common forces a geotextile experiences
during its application are tensile and puncture. The most common geotextile
testing methods are wide widthtensile testing, puncture and puncture resistance
testing, and tensile grab testing. Geotextile test specimens are generally simple to make
as they are usually just squares or rectangles cut straight from the material.
Depending on the test that will be performed on it the sample will be somewhere
between two to eight inches wide and four to eight inches long. Geotextiles
come in three basic forms: woven, punched, and heat bonded. and heat
bonded. The most common materials to make geotextiles are polypropylene and
polyester.
Keywords-Filter
fabric, testing standards, scope of accreditation, fibres ,yarn ,fabric
,terminology, significance ,sampling,conditioning and test methods
Geotextiles
are a polymers & synthetic made from textile materials named as polyester.
The Geotextiles are effectively successful materials to improve road quality.
It is divided into following types:
- Geotextile of Woven Fabrics
- Non-woven Fabrics
- Knitted Fabrics
Geotextiles are a permeable geosynthetic comprised solely of
textiles. Geotextile materials prevent the erosion of earth and similar
substances after the area has been altered due to construction usually
pertaining to civil engineering applications such as roads, pavement, bridges,
embankments and retaining walls. They allow the passage of water but not soil
and other materials.
Products
are tested for the following reasons. Products are tested for the following
reasons.
- Quality assurance and control
- Quality assurance and control
- Setting and maintaining performance standards
- Investigation of complaints
- Product developments and research
Testing
can be classified into two categories:
- Quality testing
- Performance assessment
When
to test geotextile? For any project for any civil engineering project the
design engineer must check the required specifications of geotextile material
without knowing proper specification it is very difficult to select correct
geotextile for any specific project. it is important to get the material tested
from an independent laboratory, to get correct picture. Because after using
geotextile if it fails then not only the geotextile will fail total structure
will be collapsed. That is useful to check
capabilities of textiles that will be helpful for Roads & highways. Some
testing such as Direct shear test, Compressive creep properties, Tensile Creep
and Creep Rupture Behavior, Resistance to perforation (Cone drop test),
Trapezoid tearing strength, Grab tensile strength and more.
What based on test are perform?
Testing should be done by some
methods or also known as testing standards. That is some standard set by
laboratory, institute or research centre that is given below :
- ASTM - American Society for Testing of Material- 129 STANDARDS
- ISO - International Organisation of standardization- 34 STANDARDS
- BIS - Bureau of Indian Standards -17 STANDARDS
- BS - Brittish Standard- 8 STANDARDS
- BS EN - Europian norms- 36 STANDARDS
ASTM - American Society for Testing of Material:
ASTM's textile standards provide the specifications and test
methods for the physical, mechanical, and chemical properties of textiles,
fabrics, and cloths, as well as the natural and artificial fibers that
constitute them. The textiles covered by these standards are commonly formed by
weaving, knitting, or spinning.
ISO -
International Organisation of standardization:
Today, textiles come from all over the world. They might be formed in
one country, dyed in another, and made into finished goods in yet another. To
ensure that the same practices are used in this complicated international
process, many companies follow agreed-upon standards related to industrial
processes and the goods produced by them. These standards are called ISO
textile testing standards.
following ISO standards can help to ensure consistent quality of the raw
materials being used to make textiles, which in turn improves the final
product. Adhering to ISO standards can also help lower operating costs and
ensure quality management. Following ISO standards often involves inspection
and testing at each stage of a process. For example, raw materials might be
tested, then dyed fabrics, and finally finished goods.
BIS-Bureau of Indian
Standards:
The Bureau of Indian
Standards (BIS) is the national standard organisation of India under the aegis
of Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution, Govt of India.
It was founded on 1st April 1987, replacing the Indian Standards Institute. The
Bureau is a body corporate and responsible for formulating national standards.
It comprises of members representing the Industry, Consumer Organizations,
Scientific & Research Institutes and Professional Bodies, Technical
Institutions, Central Ministries, State Governments and Members of Parliament.
The Indian Standards are formulated keeping in view national priorities,
programmes for industrial development, technological needs, export promotion,
consumer welfare, health, safety, etc. So far over 17000 standards have been
formulated in different technology areas.
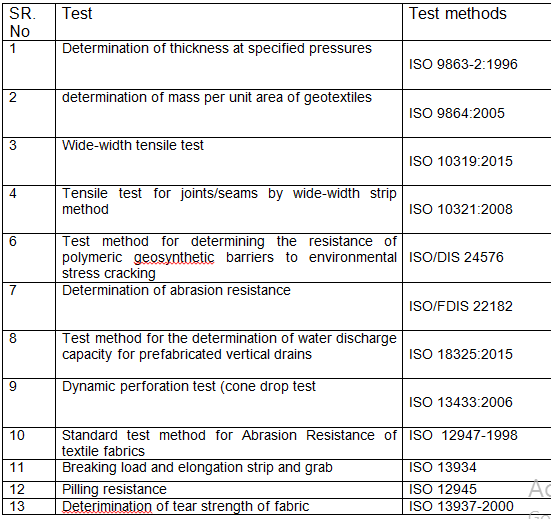
Methods used for testing of geotextile material:
- Determination of Mass per unit Area:
This
standard explains a method to determine the mass per unit area of all natural
geotextile. The mass per unit area is calculated by weighing small square
specimens of known dimensions. Ten specimens of 100cm2 are cut from the
material in such way that they are representative of the material to be tested.
The area and weight of the specimens are determined to an accuracy of 0.5 and
0.1 % respectively.
The mass
per unit area of each specimen is calculated using the equation p= (m X 106 )
/a
Where
p=mass/unit area in g/m2
m=mass of
the specimen in, g
a=the area
of the specimen in mm2
The
average mass per unit area is calculated.
- Determination of Thickness:
This
standard describes a method for the determination of the thickness of
geotextiles at specified pressures. The distances between a reference plate on
which the specimen rests and a parallel presser-foot applying the given
pressure to the specimen is define as the thickness of the geotextiles. A
thickness tester apparatus capable of exerting a pressure of 2kPa is used. Test
specimen shall be cut from the material from positions evenly distributed over
the full width and length of the sample. The specimen is placed between the
surfaces of the reference plate and pressure foot of the thickness tester. The
presserfoot is load gentle over the specimen by applying a pressure of 2±0.01
kPa. The gauge reading is noted after 30 seconds. Remove the pressure and the
specimen. The procedure is repeated for at least ten specimens. The average of
all the readings is reported as the thickness of the geotextile. The thickness
is expressed in mm to an accuracy of 1% for geotextiles thickness over 0.05mm
and to the nearest 0.001mm for thickness not exceeding 0.05mm.
- Determination of Percentage of Swell:
This
standard prescribes method for determination of the percentage of swell in
water of geo textiles after it has been immersed in water for 24 hours. Ten
specimens of size 100mmx100mm are used for the test. The thickness of each
specimens is noted on thickness tester and recorded as the initial thickness ti
to the nearest 0.01mm. Now place the specimen between the two No.17 gauge wire
mesh screens that have been soaked in water for a minimum of one hour .The
screen corners are connected loosely to hold the test specimen in place. The
test specimen is immersed in deionized water for 24 hours. After the soaking
period, the specimen is removed from the assembly after allowing the water to
drain of. The thickness of the drain specimen is measured as tf. The percentage
thickness change or swell is calculated as,
Percentage
thickness change=100(tf - ti)/ ti
The
procedure is repeated for 10 specimens.
- Determination of Water Absorption Capacity:
This
standard describes the method for determination of the water absorption
capacity of geotextiles. A galvanized screen and pans are used for this method.
Three specimens measuring 200mm x 200mm are prepared and weight the nearest
0.1g. Each specimen is placed on a tared 230mm x 230mm galvanized wire screen. Another
tared screen having similar dimension is placed over the specimen. Now both
screen and specimen is placed in a 76mm deep pan containing water at about 75mm
deep. The specimen is allowed to soak for 24 hours. After the soaking period
the specimen and the screens are allowed to drain for 10 minute and then
weighed to the nearest 0.1g. The amount of water held by the specimen is
calculated by subtracting the sum of the weights of the weighing pan, screens
and dry specimens from the total weight. The absorptive capacity is a ratio of
the water held by the specimen to the weight of the original dry specimen.
To eliminate the high degree of variability
from the Mullen Burst (3786) and Pin Puncture (4833) test methods, Static (CBR)
Puncture Strength (ASTM D 6241) was developed to replace them. CBR stands for
California Bearing Ratio, a soil strength test that was adapted for this
geotextile test. CBR Puncture is an index of puncture resistance that measures
the force required to push a flat ended plunger through a geotextile. A 150 mm
geotextile sample is secured between two steel rings. Instead of an 8 mm
diameter probe with a beveled edge (Pin Puncture 4833); this test utilizes a
50mm diameter, flat-ended probe (plunger) that is pushed slowly through the
geotextile. The relatively large size of the plunger provides a
multidirectional force on the geotextile and simulates big stones pressed onto
a geotextile laying a relatively soft sub-base.
- CBR Puncture:
To eliminate the high degree of variability
from the Mullen Burst (3786) and Pin Puncture (4833) test methods, Static (CBR)
Puncture Strength (ASTM D 6241) was developed to replace them. CBR stands for
California Bearing Ratio, a soil strength test that was adapted for this
geotextile test. CBR Puncture is an index of puncture resistance that measures
the force required to push a flat ended plunger through a geotextile. A 150 mm
geotextile sample is secured between two steel rings. Instead of an 8 mm
diameter probe with a beveled edge (Pin Puncture 4833); this test utilizes a
50mm diameter, flat-ended probe (plunger) that is pushed slowly through the
geotextile. The relatively large size of the plunger provides a
multidirectional force on the geotextile and simulates big stones pressed onto
a geotextile laying a relatively soft sub-base.
- Permittivity:
Permittivity
is the mechanism by which water moves through the fabric. The permittivity test
measures the quantity of water which can pass through a geotextile
perpendicular to the surface of the geotextile. The permittivity may be
measured either in a constant head or falling head test, although constant head
testing is more common due to the high flow rates through geotextiles which
make it is difficult to obtain readings of head change versus time in the
falling head test. In the constant head test, a head of 50 mm water is
maintained on the geotextile throughout the test. The quantity of flow is
measured versus time. In the falling head test, a column of water is allowed to
flow through the geotextile and reading of head changes versus time is taken.
The flow rate of water through the geotextile needs to be slow enough to obtain
accurate readings.
The Bombay Textile Research
Association (BTRA) was registered by members of the Millowners' Association,
Bombay, under the Societies Registration Act, XXI of 1860 on 21st April 1954,
with nine mill companies contributing to the Memorandum and Articles of
Association. In the past 25 years many applications of geosynthetics have
proved their value in civil engineering projects and this new class of material
has added entirely a new dimension to the world of geotechnical engineering.
Geosynthetic materials like Geotextiles, Geogrids, Geonets, Geocell, and
Geomembranes are used in various civil engineering activities especially in
highway engineering to facilitate construction, ensure better performance of
the structure and reduce maintenance. To know the performance of these
products, performance evaluation is to be done & to meet the requirements,
quality has to be maintained.
The standard is not directly
concerned with the actual properties or design of product but with gaureenting
that the product is always manufactured in the same way, to the same
specifications, that no substandard raw material used in the production and
that any rejects do not find their way into the output. The concerns of the
standard are really with good organizational practice and it involves complete
documentation of the whole process together with internal and external checks
to ensure that everything is being run according to these written instructions.
Testing staff having skill
in sample preparation, handling of test equipments, knowledge of quality system
and test standards. Experience in testing of similar products & various
tests will have better influence on quality of testing. The staffs are trained
time to time for various tests, quality control systems and interpretation of
results. Calibration of test equipments is done periodically ( every year ).
Quality audit is carried out by NABL every year. The Laboratory implements new or
revised test.
Common Tests of Geotextile:
- Mass : gms per meter square
- Thickness at specified pressure
- Tensile strength : Strip / Grab / Wide Width
- Tear Strength : Trapezoid
- Water Permeability : Vertical / Horizontal
- Apparent Opening Size : Sieving method
- Puncture Resistance : CBR / Index / Cone
It is
pertinent to mention that BTRA is the first institute in India and probably
only the third institute outside USA to get this coveted accreditation. What
this means to the geosynthetics producers and users is that they can get the
products tested in BTRA with utmost confidence that the accuracy of the results
are as good as any other GAI-LAP accredited laboratories. They can get the
tests done in India, thus saving time and money without compromising on the
quality of the results.
Result and Disscusion:
Considering
environmental impact, geotextiles should be collected from the project site.
The test which we normally do in isolation that may not be suitable for most of
the geotextile testing. So, we have to get the sample collected from the exact
site and then the sample should be tested in the laboratory. Now there are
standards for collection of test specimens. (Refer Slide Time: 13:26) So, this
standards are ASTM D4354 which is standard practice for sampling of geo
synthetics for testing, then ISO 554 which is specifying the standard
atmosphere for conditioning and or testing specifications ISO 9862 Geotextile
sampling and preparation of test specimen. So, during production and
construction time, test specimens are collected at specified interval. The
number of specimens to be collected for testing is given in the concerned
standard. So, we have to collect the specimen from the site.
So, there
are two different types of test which are conducted on geotextiles. One is
called index testing or in isolation test, which actually test in the
laboratory condition. So, only the tests are performed on geotextile next is
that its called performance test what is that? The performance test are
performed along with site specified soil and conditions. So, index test will
only give an idea and comparative value between the geotextiles which is good
or which is bad comparatively, but the better geotextiles as per index test may
not perform well in performance test. Because in performance test we have to
test along with the site specified soil and site specified condition. So, there
are different types of tests conducted on geotextile materials, these are
physical testing, mechanical test, hydraulic test, endurance test degradation
test. So, we were discuss each and every methods.
Conclusion:
- test methods are a means to understand the product
- test results give a true picture of the product
- test results are dependable when conducted exactly as per the standard
- methods for testing of geotextile materials is important for determine the properties of geotextile materials. The properties are affected on construction in where use of materialthat’s mean a testing should done best way and without any errors. Hence these paper describe the all information for testing of geotextile.
References:
- Geotextiles - TestResources
- www.technotex.gov.in › TES...PPT
- Web results
- TEST METHODS FOR GEOTEXTILES
- https://www.astm.org › Standards
- ASTM D4595 - 17 Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Geotextiles by
- https://nptel.ac.in › Lecture-8PDF
- Web results
- Testing of Geosynthetics - Nptel










5 Comments
Nice content.
ReplyDeleteNice piece of information and really informative stats!
ReplyDeleteLay bhari, kdk bhava
ReplyDeleteUseful article
ReplyDeleteVery informative 👍
ReplyDeleteNew comments are not allowed.